This primer explains the major components found inside a Sanyo Denki Uninterruptable Power Supply (UPS). These principal components make up the system requirements for a Double Conversion Online topology. There are several options and configuration available; this article will cover only a high-level view of basic operations of a Double Conversion Online UPS. The four main components to be covered are the rectifier, battery, inverter and bypass switch.
Double Conversion Online UPS
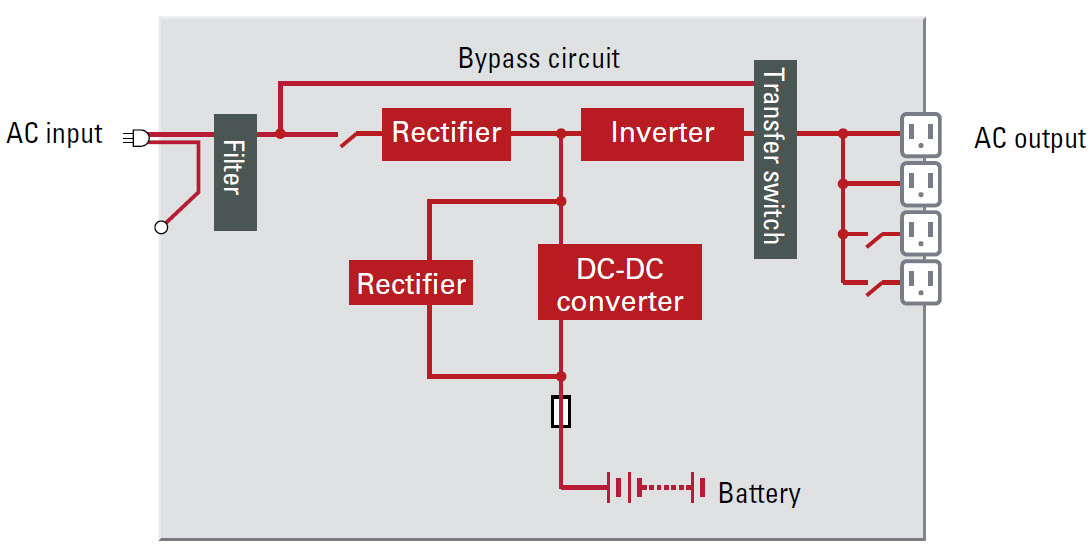 As the name suggests, the UPS takes incoming power and converts it twice before finally supplying electrical power to the attached equipment. Inbound electrical power, either provided by an electrical utility or on-site power generation will first enter through the UPS’ rectifier. The wide input rectifier converts the supplied AC power to DC power. The internal battery is charged and kept in a “ready state” from power received from the DC bus. The DC power is then routed to the inverter, converting the DC power back to AC and then supplied to electrical equipment connected to the UPS for both power conditioning as well as back-up power protection. If the internal system diagnostics detect issues with the UPS, the static switch will close the circuit, routing power away from the rectifier, battery, and inverter allowing connected equipment to remain powered and operational.
As the name suggests, the UPS takes incoming power and converts it twice before finally supplying electrical power to the attached equipment. Inbound electrical power, either provided by an electrical utility or on-site power generation will first enter through the UPS’ rectifier. The wide input rectifier converts the supplied AC power to DC power. The internal battery is charged and kept in a “ready state” from power received from the DC bus. The DC power is then routed to the inverter, converting the DC power back to AC and then supplied to electrical equipment connected to the UPS for both power conditioning as well as back-up power protection. If the internal system diagnostics detect issues with the UPS, the static switch will close the circuit, routing power away from the rectifier, battery, and inverter allowing connected equipment to remain powered and operational.
RECTIFIER
The electrical power provided by the utility supplier first enters the UPS’ rectifier. The rectifier will convert the incoming Alternating Current (AC) power to Direct Current (DC) electricity. This conversion allows for the internal (DC) battery to charge. Because the rectifier is wide input, it handles wide power fluctuations without having to engage the UPS batteries during a power event. Along with battery charging, the DC power then routes to the inverter.
BATTERY
 The UPS utilizes rechargeable VRLA (Valve Regulated Lead Acid) batteries. VRLA batteries recombine hydrogen and oxygen during the charging process, drastically reducing the amount of gassing of the battery, as seen with other battery chemistries. Normal room ventilation is sufficient to remove any hydrogen during operation, so special ventilation is not required. Additionally, the batteries electrolyte is immobilized in gel giving them the ability to be installed in any orientation and are classified as non-hazardous, non-spill-able, and will meet the requirements of air transportation (IATA).
The UPS utilizes rechargeable VRLA (Valve Regulated Lead Acid) batteries. VRLA batteries recombine hydrogen and oxygen during the charging process, drastically reducing the amount of gassing of the battery, as seen with other battery chemistries. Normal room ventilation is sufficient to remove any hydrogen during operation, so special ventilation is not required. Additionally, the batteries electrolyte is immobilized in gel giving them the ability to be installed in any orientation and are classified as non-hazardous, non-spill-able, and will meet the requirements of air transportation (IATA).
INVERTER
 In the final stage of power processing, the UPS’ solid state inverter takes DC power either from the DC bus under normal operations or battery during a power outage and converts it back to AC power. At this time the power is also conditioned providing a pure sine waveform for final output to target equipment attached to the UPS.
In the final stage of power processing, the UPS’ solid state inverter takes DC power either from the DC bus under normal operations or battery during a power outage and converts it back to AC power. At this time the power is also conditioned providing a pure sine waveform for final output to target equipment attached to the UPS.
STATIC BYPASS SWITCH
In the event of the UPS system failing, the internal static bypass switch will automatically close the circuit and will divert the incoming AC power around the rectifier, batteries and the inverter to continue to supply utility provided power directly to your equipment. While this provided power will not be conditioned this feature will continue to supply electrical power to target equipment, keeping them online while the UPS can be repaired or replaced.